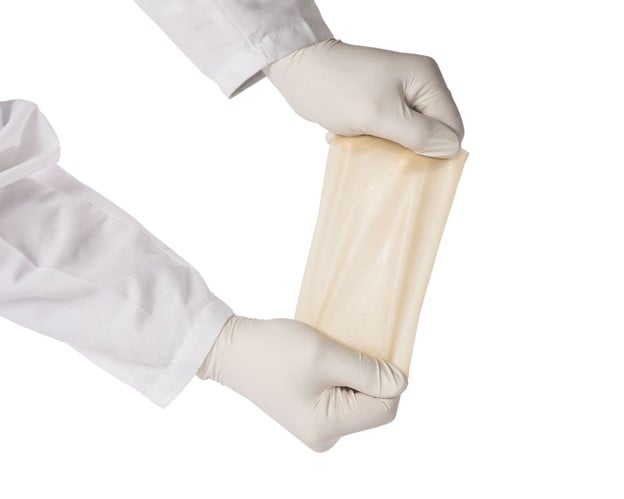
CYTAL® WOUND AND CYTAL® BURN MATRIX
Cytal is the sheet form of UBM Technology intended for wound management. It is available in a variety of sizes and thicknesses.
MICROMATRIX® UBM PARTICULATE
MicroMatrix is the particulate form of UBM Technology intended for wound management. It is available in fine and regular configurations.
MICROMATRIX® FLEX
Flex is a dual-syringe system designed to enable convenient mixing and delivery of MicroMatrix paste to hard-to-reach wound areas.
GENTRIX® SURGICAL MATRIX
Gentrix is intended for implantation to reinforce soft tissue where weakness exists in patients requiring gastroenterological or plastic & reconstructive surgery.
UBM devices are manufactured by harvesting and minimally processing porcine bladders.
This preserves the integrity of essential structures and molecular components so that only two distinct layers remain:.png?width=1050&height=549&name=UBM%20provides%20an%20environment%20where%20the%20body%20is%20more%20likely%20to%20exhibit%20a%20higher%20ratio%20of%20M2%20to%20M1%20macrophages%2c3%2c7%20which%20has%20been%20shown%20to%20facilitate%20the%20remodeling%20of%20site-appropriate%20tissue.3%20(3).png)
Characteristics of UBM
UBM devices are biologically-derived, three-dimensional scaffolds, which contain a collection of collagens and other proteins including laminin, proteoglycans,1 and numerous growth factors.2
The resulting product is:
- Non-crosslinked
- Resorbable
- Decellularized

Cellular Responses to UBM
After a UBM device is placed in the body, white blood cells including macrophages and neutrophils will enter the UBM scaffold to initiate the remodeling response. Fibroblasts will also enter the scaffold, depositing various collagens that provide strength and structure for the new tissue, and new blood vessels will form transporting blood and nutrients to the site of repair.3-6
UBM provides an environment where the body is more likely to exhibit a higher ratio of M2 to M1 macrophages,3,7 which has been shown to facilitate the remodeling of site-appropriate tissue.3
UBM supports the development of healthy tissue that mimics the structure and biomechanical functionality of the surrounding anatomy. Over time, the devices will fully resorb and completely remodel into the host tissue, leaving no foreign body.3-6
10+ YEARS IN THE MARKETPLACE
200+ PRE-CLINICAL AND CLINICAL
PUBLICATIONS
For product information, including indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and potential adverse effects, see the package insert and Integra’s website:
FAQs
What is ACell?
ACell was a Columbia, Maryland-based biotechnology company, working in regenerative medicine. The company was founded in 1999 by Alan R. Spievack, a former associate professor at Harvard Medical School.
What is UBM?
UBM technology is based on the research of ACell’s founder, the late Alan Spievack, MD. Dr. Spievack, inspired by the regenerative capabilities of salamanders, studied cell regeneration and extracellular matrices (ECMs), ultimately leading to the development of UBM technology. UBM is the technology behind Cytal® Wound and Cytal® Burn Matrix, MicroMatrix® UBM Particulate and Gentrix® Surgical Matrix.
What is Integra's role?
Integra LifeSciences Holdings Corporation acquired ACell in January 2021. Read the press release here.
Contact your Integra sales representative for information and ordering details on Cytal® Wound and Cytal® Burn Matrix, MicroMatrix® UBM Particulate and Gentrix® Surgical Matrix. For the UBM veterinary portfolio, visit www.integraveterinary.com.
2. Data on file, MEMO-1108, multiplex ELISA testing from lots (n=4) of MicroMatrix.
3. Brown BN, Londono R, Tottey S, Zhang L, Kukla KA, Wolf MT, Daly KA, Reing JE, Badylak SF†. Macrophage phenotype as a predictor of constructive remodeling following the implantation of biologically derived surgical mesh materials. Acta Biomaterialia. 2012; 8:978-987.
4. Sasse KC, Lambin JH, Gevorkian J, et al. Long-term clinical, radiological, and histological follow-up after complex ventral incisional hernia repair using urinary bladder matrix graft reinforcement: a retrospective cohort study. Hernia. 2018;22(6):899-907.
5. Riganti JM, Ciotola F, Amenabar A, Craiem D, Graf S, Badaloni A, Gilbert TW*, Nieponice A‡. Urinary bladder matrix scaffolds strengthen esophageal hiatus repair. Journal of Surgical Research. 2016; 204:344-50.
6. Young DA, Jackson N, Ronaghan CA, Brathwaite CEM, Gilbert TW. Retrorectus repair of incisional ventral hernia with urinary bladder matrix reinforcement in a long-term porcine model. Regenerative Medicine. 2018; doi:10.2217/rme-2018-0023.
7. Paige JT, et al. Modulation of inflammation in wounds of diabetic patients treated with porcine urinary bladder matrix. Regenerative Medicine. 2019 May;14(4):269-277. doi:10.2217/rme-2019-0009. Epub 2019 Apr 25.
ACell, MicroMatrix, Cytal, Gentrix, Integra and the Integra logo are registered trademarks of Integra LifeSciences Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. ©2024 Integra LifeSciences Corporation. All rights reserved. 3976377-2-EN




.png)